BoxLayout class:
| The BoxLayout is used to arrange the components either vertically or horizontally. For this purpose, BoxLayout provides four constants. They are as follows: |
Note: BoxLayout class is found in javax.swing package.
Fields of BoxLayout class:
|
Constructor of BoxLayout class:
Example of BoxLayout class with Y-AXIS: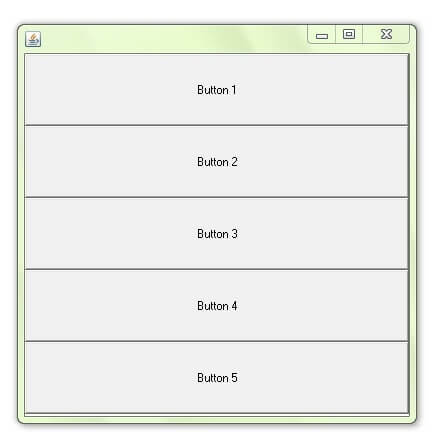
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; public class BoxLayoutExample1 extends Frame { Button buttons[]; public BoxLayoutExample1 () { buttons = new Button [5]; for (int i = 0;i<5;i++) { buttons[i] = new Button ("Button " + (i + 1)); add (buttons[i]); } setLayout (new BoxLayout (this, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); setSize(400,400); setVisible(true); } public static void main(String args[]){ BoxLayoutExample1 b=new BoxLayoutExample1(); } } Example of BoxLayout class with X-AXIS: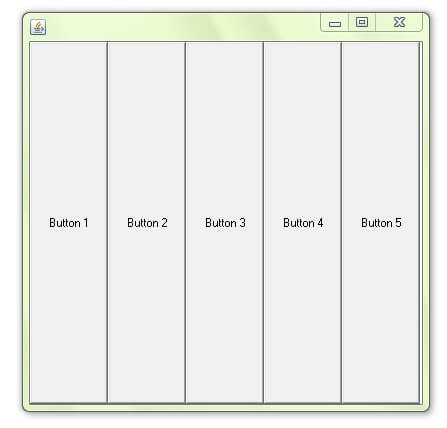
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; public class BoxLayoutExample2 extends Frame { Button buttons[]; public BoxLayoutExample2() { buttons = new Button [5]; for (int i = 0;i<5;i++) { buttons[i] = new Button ("Button " + (i + 1)); add (buttons[i]); } setLayout (new BoxLayout(this, BoxLayout.X_AXIS)); setSize(400,400); setVisible(true); } public static void main(String args[]){ BoxLayoutExample2 b=new BoxLayoutExample2(); } } |
No comments:
Post a Comment