A java package is a group of similar types of classes, interfaces and sub-packages.
Package in java can be categorized in two form, built-in package and user-defined package.
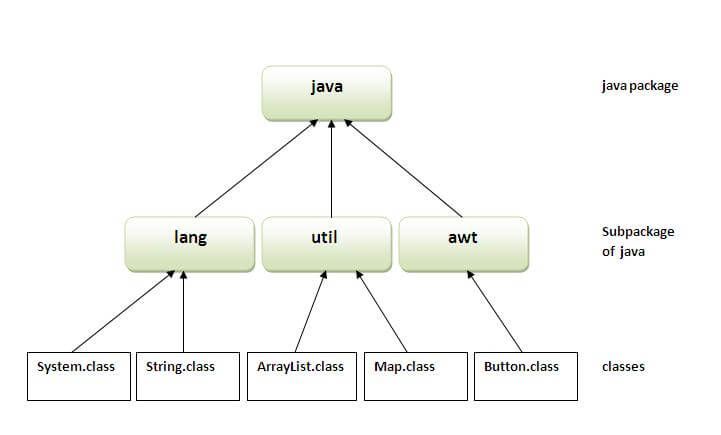
There are many built-in packages such as java, lang, awt, javax, swing, net, io, util, sql etc.
Here, we will have the detailed learning of creating and using user-defined packages.
Advantage of Java Package
1) Java package is used to categorize the classes and interfaces so that they can be easily maintained.
2) Java package provides access protection.
3) Java package removes naming collision.
 Simple example of java package
The package keyword is used to create a package in java.
How to compile java package
If you are not using any IDE, you need to follow the syntax given below:
For example
The -d switch specifies the destination where to put the generated class file. You can use any directory name like /home (in case of Linux), d:/abc (in case of windows) etc. If you want to keep the package within the same directory, you can use . (dot).
How to run java package program
You need to use fully qualified name e.g. mypack.Simple etc to run the class.
Output:Welcome to package
How to access package from another package?
1) Using packagename.*
Example of package that import the packagename.*Output:Hello 2) Using packagename.classname
If you import package.classname then only declared class of this package will be accessible.
Example of package by import package.classnameOutput:Hello 3) Using fully qualified name
If you use fully qualified name then only declared class of this package will be accessible. Now there is no need to import. But you need to use fully qualified name every time when you are accessing the class or interface.
It is generally used when two packages have same class name e.g. java.util and java.sql packages contain Date class.
Example of package by import fully qualified nameOutput:Hello Note: If you import a package, subpackages will not be imported.
If you import a package, all the classes and interface of that package will be imported excluding the classes and interfaces of the subpackages. Hence, you need to import the subpackage as well.
Note: Sequence of the program must be package then import then class.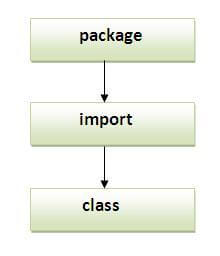 Subpackage in java
Package inside the package is called the subpackage. It should be created to categorize the package further.
Let's take an example, Sun Microsystem has definded a package named java that contains many classes like System, String, Reader, Writer, Socket etc. These classes represent a particular group e.g. Reader and Writer classes are for Input/Output operation, Socket and ServerSocket classes are for networking etc and so on. So, Sun has subcategorized the java package into subpackages such as lang, net, io etc. and put the Input/Output related classes in io package, Server and ServerSocket classes in net packages and so on.
The standard of defining package is domain.company.package e.g. com.javatpoint.bean or org.sssit.dao.Example of Subpackage
Output:Hello subpackage How to send the class file to another directory or drive?
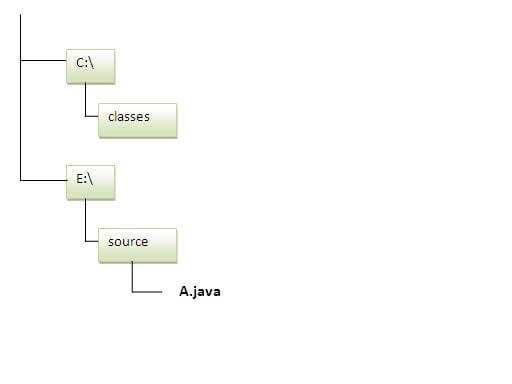 To Compile:
To Run:
Another way to run this program by -classpath switch of java:
Output:Welcome to package Ways to load the class files or jar files
Rule: There can be only one public class in a java source file and it must be saved by the public class name.How to put two public classes in a package?
What is static import feature of Java5?
What about package class?
|
Sunday, 12 April 2015
Java Package
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment